-Ramesh Bacha
What is Maven?
......................................................................................................................................
Ø Introduction
Maven, a Yiddish word meaning accumulator of knowledge, was originally started as an attempt to simplify the build processes in the Jakarta Turbine project. There were several projects each with their own Ant build files that were all slightly different and JARs were checked into CVS. We wanted a standard way to build the projects, a clear definition of what the project consisted of, an easy way to publish project information and a way to share JARs across several projects.
The result is a tool that can now be used for building and managing any Java-based project. We hope that we have created something that will make the day-to-day work of Java developers easier and generally help with the comprehension of any Java-based project.
Ø Maven's Objectives
Maven's primary goal is to allow a developer to comprehend the complete state of a development effort in the shortest period of time. In order to attain this goal there are several areas of concern that
Maven attempts to deal with:
• Making the build process easy
• Providing a uniform build system
• Providing quality project information
• Providing guidelines for best practices development
• Allowing transparent migration to new features
Ø Making the build process easy
While using Maven doesn't eliminate the need to know about the underlying mechanisms, Maven does provide a lot of shielding from the details.
Ø Providing a uniform build system
Maven allows a project to build using its project object model (POM) and a set of plugins that are shared by all projects using Maven, providing a uniform build system. Once you familiarize yourself with how one Maven project builds you automatically know how all Maven projects build saving you immense amounts of time when trying to navigate many projects.
Ø Providing quality project information
Maven provides plenty of useful project information that is in part taken from your POM and in part generated from your project's sources. For example, Maven can provide:
• Change log document created directly from source control
• Cross referenced sources
• Mailing lists
• Dependency list
• Unit test reports including coverage
As Maven improves the information set provided will improve, all of which will be transparent to users of Maven. Other products can also provide Maven plugins to allow their set of project information alongside some of the standard information given by Maven, all still based on the POM.
Ø Providing guidelines for best practices development
Maven aims to gather current principles for best practices development, and make it easy to guide a project in that direction. For example, specification, execution, and reporting of unit tests are part of the normal build cycle using Maven. Current unit testing best practices were used as guidelines:
• Keeping your test source code in a separate, but parallel source tree
• Using test case naming conventions to locate and execute tests
• Have test cases setup their environment and don't rely on customizing the build for test preparation.
Maven also aims to assist in project workflow such as release management and issue tracking.
Maven also suggests some guidelines on how to layout your project's directory structure so that once you learn the layout you can easily navigate any other project that uses Maven and the same defaults.
Ø Allowing transparent migration to new features
Maven provides an easy way for Maven clients to update their installations so that they can take advantage of any changes that been made to Maven itself. Installation of new or updated plugins from third parties or Maven itself has been made trivial for this reason.
Ø What is Maven Not?
You may have heard some of the following things about Maven:
• Maven is a site and documentation tool
• Maven extends Ant to let you download dependencies
• Maven is a set of reusable Ant scriptlets
While Maven does these things, as you can read above in the "What is Maven?" section, these are not the only features Maven has, and its objectives are quite different.
Maven does encourage best practices, but we realise that some projects may not fit with these ideals for historical reasons. While Maven is designed to be flexible, to an extent, in these situations and to the needs of different projects, it can not cater to every situation without making compromises to the integrity of its objectives.
If you decide to use Maven, and have an unusual build structure that you cannot reorganise, you may have to forgo some features or the use of Maven altogether.
Maven Basics
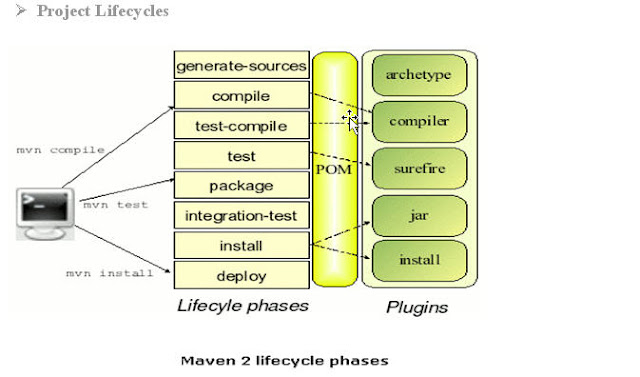
Ø The Project Object Model (POM)
• The heart of a Maven project is the POM
• Contains meta-data information of the project
• Versioning and configuration management
• Dependencies
• Project structure
• Application and testing resources
• Placed in project home directory as “pom.xml”
Ø POM.XML
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.Ascential.com</groupId>
<artifactId>ASB-master</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>ASB master project</name>
<url>http://www.ascential.com/</url>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Feature Summary
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following are the key features of Maven in a nutshell:
• Simple project setup that follows best practices - get a new project or module started in seconds
• Consistent usage across all projects means no ramp up time for new developers coming onto a project
• Superior dependency management including automatic updating, dependency closures (also known as transitive dependencies)
• Able to easily work with multiple projects at the same time
• A large and growing repository of libraries and metadata to use out of the box, and arrangements in place with the largest Open Source projects for real-time availability of their latest releases
• Extensible, with the ability to easily write plugins in Java or scripting languages
• Instant access to new features with little or no extra configuration
• Ant tasks for dependency management and deployment outside of Maven
• Model based builds: Maven is able to build any number of projects into predefined output types such as a JAR, WAR, or distribution based on metadata about the project, without the need to do any scripting in most cases.
• Coherent site of project information: Using the same metadata as for the build process, Maven is able to generate a web site or PDF including any documentation you care to add, and adds to that standard reports about the state of development of the project. Examples of this information can be seen at the bottom of the left-hand navigation of this site under the "Project Information" and "Project Reports" submenus.
• Release management and distribution publication: Without much additional configuration, Maven will integrate with your source control system such as CVS and manage the release of a project based on a certain tag. It can also publish this to a distribution location for use by other projects. Maven is able to publish individual outputs such as a JAR, an archive including other dependencies and documentation, or as a source distribution.
• Dependency management: Maven encourages the use of a central repository of JARs and other dependencies. Maven comes with a mechanism that your project's clients can use to download any JARs required for building your project from a central JAR repository much like Perl's CPAN. This allows users of Maven to reuse JARs across projects and encourages communication between projects to ensure that backward compatibility issues are dealt with.
References




No comments:
Post a Comment